Thematic analysis is a widely used method in qualitative research that involves identifying patterns, themes, and meanings within data. It provides a flexible yet structured approach to analyzing textual information, making it a valuable tool for researchers across various disciplines. Thematic analysis is commonly used in psychology, social sciences, and market research, offering insights into human behavior, attitudes, and experiences. This article explores its definition, key steps, applications, challenges, and tools used in its implementation.
What is thematic analysis, and how is it defined in qualitative research?
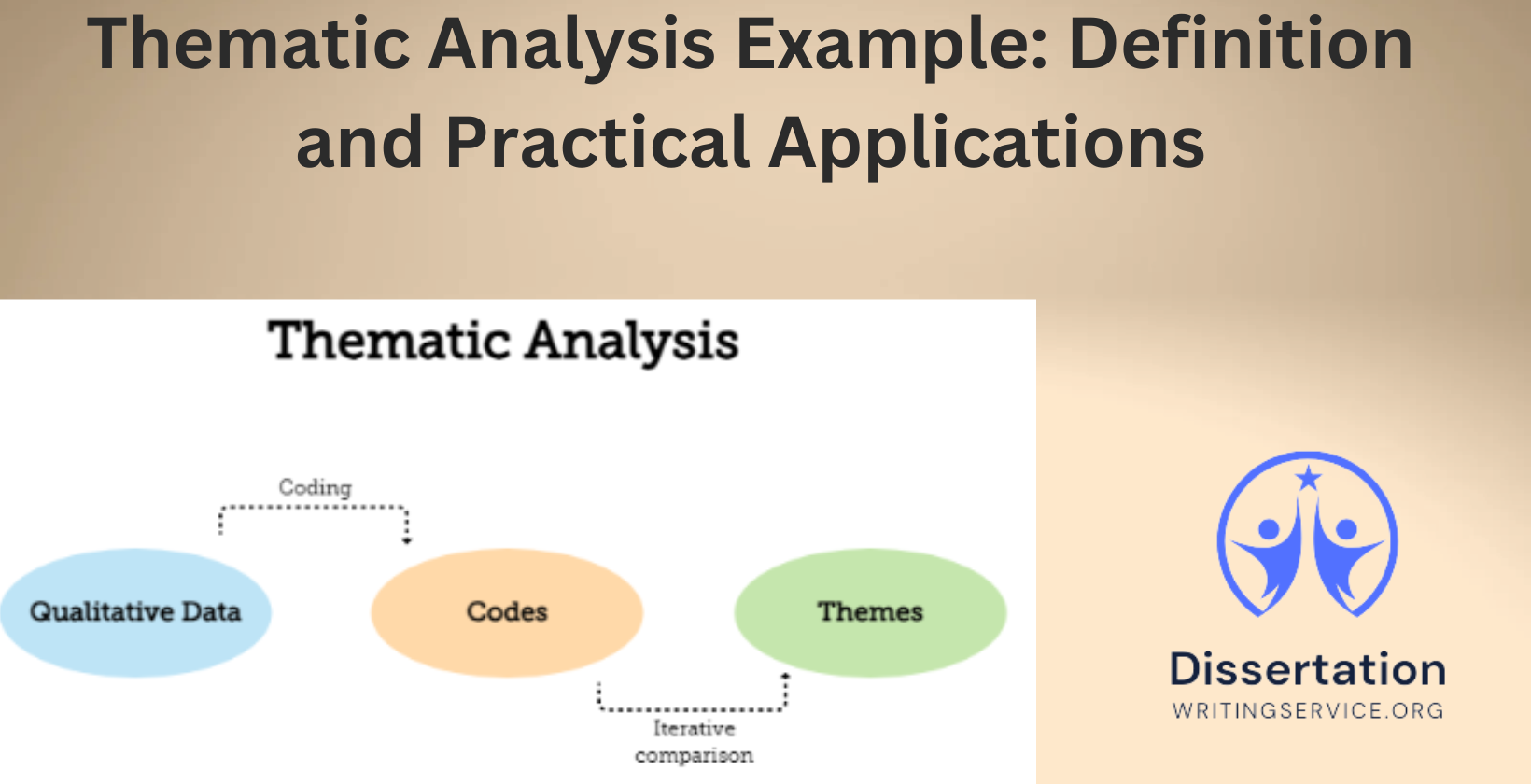
Thematic analysis is a qualitative research method used to identify, analyze, and report patterns within data. It provides a structured yet flexible way to examine large amounts of text, such as interviews, focus groups, or written documents. According to Braun and Clarke (2006), thematic analysis involves systematically identifying themes that represent key aspects of the data set. It allows researchers to interpret qualitative data by categorizing it into meaningful themes that address the research question.
How does thematic analysis differ from other qualitative research methods?
Thematic analysis differs from other qualitative research methods in its flexibility and focus on theme identification. Grounded theory involves developing theories from data, while discourse analysis examines language use and communication patterns. Narrative analysis focuses on personal stories and experiences, whereas content analysis quantifies data by categorizing words or phrases. Thematic analysis prioritizes theme identification without strict adherence to a specific theoretical framework, making it adaptable across various disciplines.
What are the key steps involved in conducting a thematic analysis?
The key steps involved in conducting a thematic analysis include:
- Familiarization with data – Researchers read and review the data multiple times to gain an in-depth understanding.
- Generating initial codes – Data segments are systematically coded to capture important features.
- Searching for themes – Codes are grouped into potential themes that represent key patterns.
- Reviewing themes – Themes are refined by comparing them against the data set to ensure consistency.
- Defining and naming themes – Each theme is clearly defined to capture its essence.
- Producing the final report – Findings are documented, supported by examples, and interpreted in relation to the research question.
How can researchers ensure the reliability and validity of themes identified during analysis?
Researchers can ensure the reliability and validity of themes by using triangulation, inter-rater reliability, and member checking. Triangulation involves comparing findings across different data sources. Inter-rater reliability ensures consistency by having multiple researchers code the same data. Member checking involves verifying themes with participants to confirm accuracy. Transparency in the coding process and clear documentation of decisions further enhance validity.
In what ways can thematic analysis be applied across different fields of study?
Thematic analysis can be applied in psychology, sociology, business, education, and healthcare research. In psychology, it helps understand mental health experiences. In business, it analyzes customer feedback and employee satisfaction. In education, it evaluates student learning experiences. In healthcare, it examines patient narratives and treatment outcomes. Each field benefits from thematic analysis by uncovering underlying themes in qualitative data.
What are common challenges faced during thematic analysis, and how can they be addressed?
Common challenges in thematic analysis include data overload, researcher bias, and difficulty in theme identification. Data overload can be managed by setting clear research questions and focusing on relevant data. Researcher bias is reduced through reflexivity, peer review, and coding audits. Difficulty in theme identification is addressed by iteratively refining codes and themes while ensuring alignment with the data.
How does one differentiate between codes and themes in the context of thematic analysis?
Codes are basic units of meaning that describe specific aspects of data, while themes represent broader patterns formed by multiple codes. A code captures a single idea, such as “job dissatisfaction,” whereas a theme groups related codes under a broader concept like “workplace challenges.” Themes provide a higher-level interpretation of the data, allowing researchers to construct meaningful narratives.
What tools or software are available to assist in conducting thematic analysis?
Software tools available for thematic analysis include NVivo, ATLAS.ti, MAXQDA, and Dedoose. NVivo enables efficient coding and visualization of themes. ATLAS.ti provides advanced text analysis and network visualization. MAXQDA offers interactive tools for categorizing and analyzing qualitative data. Dedoose is a cloud-based platform suitable for collaborative research. These tools enhance accuracy, organization, and efficiency in qualitative analysis.
How can thematic analysis be utilized to interpret complex qualitative data effectively?
Thematic analysis is utilized to interpret complex qualitative data effectively by systematically coding, categorizing, and synthesizing information into themes. Large datasets are broken down into manageable units, allowing researchers to identify connections and patterns. The iterative process ensures themes accurately reflect participant experiences. Clear documentation, visualization, and integration of multiple perspectives further enhance data interpretation.
What are some real-world examples where thematic analysis has been successfully implemented?
Thematic analysis has been successfully implemented in mental health research, consumer behavior studies, and policy evaluation. In mental health research, thematic analysis has been used to explore experiences of individuals with anxiety disorders. In consumer behavior studies, it has analyzed customer feedback to improve service quality. In policy evaluation, thematic analysis has assessed public perceptions of government initiatives. These applications demonstrate its effectiveness in deriving meaningful insights from qualitative data.